The Khalistan Map is a controversial and highly emotive subject that has remained a topic of significant debate and contention for several decades. This map represents the proposed independent Sikh state of Khalistan, which Sikh separatist movements have advocated for in various forms since the early 20th century. This article aims to provide an overview of the Khalistan Map, its historical context, and its contemporary implications.
Historical Background
The roots of the Khalistan movement can be traced back to the early 20th century when some Sikh leaders began to express dissatisfaction with the status of Sikhs within India.
Many Sikhs feel deprived of an independent nation when the subcontinent was partitioned in 1947. With a rich history in the Punjab region and a distinct religious identity, Sikhs aspired for self-rule. However, the traumatic partition of India, which left Punjab divided along religious lines, disrupted their cultural fabric. This sense of injustice and unfulfilled aspirations contributed to the Khalistan movement, with Sikhs seeking an independent state to protect their identity.
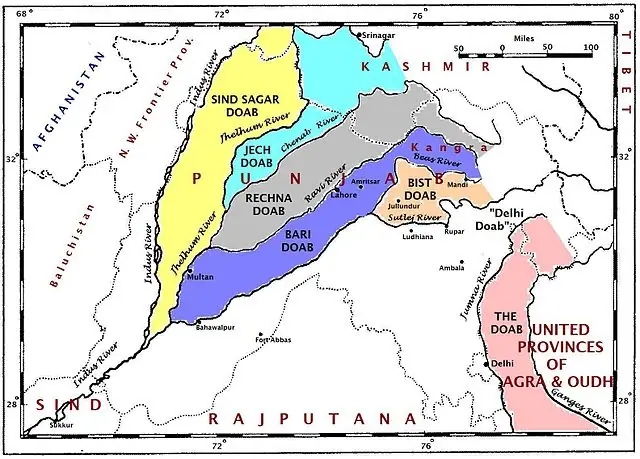
The demand for Khalistan, an independent Sikh state, gained prominence in the 1970s and 1980s during a period marked by political unrest and violence in Punjab, India. Sikhs believed that their representation in the Indian political system is inadequate and sought to establish a separate homeland where they could exercise their rights and preserve their distinct cultural and religious identity.
The Khalistan Map
The Khalistan Map is a representation of the proposed boundaries of the Sikh state of Khalistan. However, it is essential to note that there is no universally agreed-upon Khalistan Map. Different Sikh groups and organizations have proposed various versions of the map over the years. These maps typically include the Indian state of Punjab and some adjoining areas with significant Sikh populations.
The most commonly cited regions in the Khalistan Map include:
Punjab: The heartland of Sikhism and the epicenter of the Khalistan movement, Punjab, is the primary focus of the proposed Khalistan state.
Haryana: Some versions of the Khalistan Map extend into Haryana, a neighboring state with a significant Sikh population.
Parts of Himachal Pradesh: A few Khalistan maps also incorporate areas of Himachal Pradesh, another state with a Sikh presence.
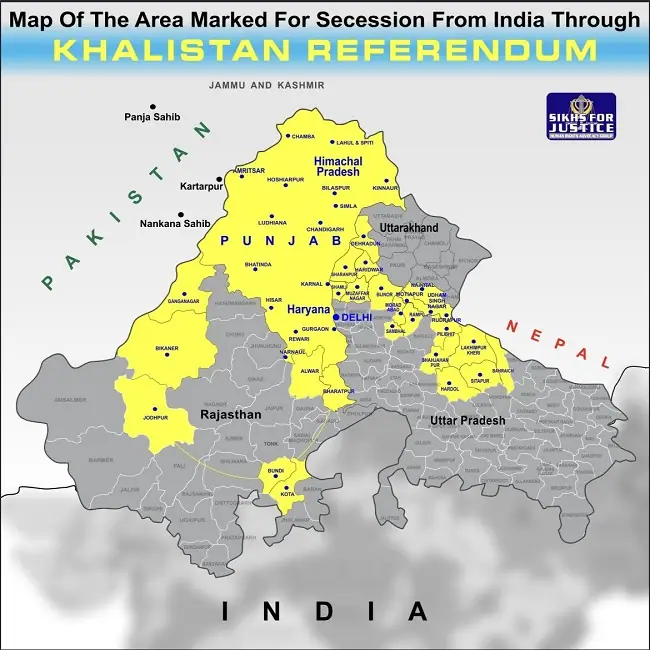
Khalistan Map: Sikh For Justice Version
In October 2021, the US-based Sikh For Justice (SFJ) released a map of Khalistan. It encompasses not only Punjab but also extends into Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, and several districts of Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh.
Contemporary Implications
The Khalistan Map remains a highly sensitive issue in India and among the Sikh diaspora worldwide. Its contemporary implications are complex and multifaceted:
Legal Status: The Indian government officially considers the demand for Khalistan and the Khalistan Map as separatist and illegal. Any attempts to promote or disseminate these ideas within India are met with legal action.
Political Landscape: The Khalistan movement has influenced the political landscape of Punjab. It has been a significant factor in state elections. While the demand for Khalistan has lost some of its earlier momentum, it still resonates with a section of the Sikh population.
Diaspora Activism: Sikh communities in countries such as Canada, the United Kingdom, and the United States continue to engage in activism and advocacy related to Khalistan. This includes protests, lobbying, and raising awareness about their perceived grievances. The Khalistan Movement in Canada is particularly strong. The Killing of the Canada-based Khalistani leader Hardeep Singh Nijjar in June 2023 has created tension between Canada and India in recent times.
Security Concerns: The Indian government maintains a vigilant stance regarding Khalistan-related activities, viewing them as potential threats to national security. Security agencies closely monitor any signs of separatist movements or violence.
International Diplomacy: The issue of Khalistan occasionally emerges in international diplomacy, with some countries expressing concern over human rights issues in Punjab and the treatment of Sikhs in India.
Summary of the “Khalistan Map”
In conclusion, the Khalistan Map represents a complex and contentious issue with deep historical roots. While the demand for Khalistan has evolved over time and lost some of its earlier intensity, it continues to be a source of concern and debate in India and among the Sikh diaspora. Understanding the historical context and contemporary implications of the Map is crucial for a balanced and informed perspective on this sensitive topic.