The BMP-3 infantry fighting vehicle (IFV) emerged as a groundbreaking Soviet creation in the late 1970s. Originally designed as a successor to the PT-76 amphibious light tank, it underwent a transformation during development, emerging as an agile and well-armed infantry fighting vehicle. Adopted by the Soviet Army in 1987, the BMP-3 boasted significant improvements over its predecessors, though it faced challenges regarding reliability in its early stages.
Global Reach
Despite some initial setbacks, the BMP-3 found its way into the hands of the Russian military, where it served alongside the BMP-2. However, it did not achieve the same level of numerical dominance. By 2017, approximately 720 BMP-3 vehicles were in Russian service, with another 200 on order. Beyond Russia, the BMP-3 became a commercial success, with exports to nations like Azerbaijan, Cyprus, Indonesia, Kuwait, South Korea, the United Arab Emirates, and Venezuela. Morocco also ordered a substantial number of these versatile combat vehicles.
BMP-3: Design and Appearance
The BMP-3’s appearance differs significantly from the BMP-1 and BMP-2, resembling a light tank.
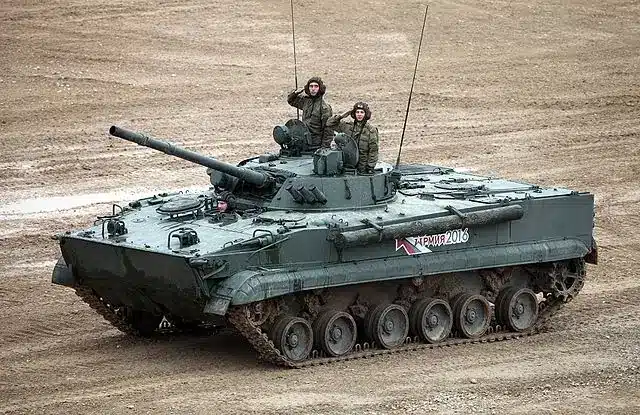

This transformation was driven by a desire for improved protection and amphibious capabilities. Its rear-mounted engine enhances weight distribution and enhances its ability to traverse water obstacles.
Firepower
At the heart of the BMP-3’s firepower is a formidable 100 mm gun capable of firing 9M117 Bastion laser-guided anti-armor missiles, as well as standard HE-FRAG projectiles. These missiles offer impressive anti-armor capabilities with a maximum range of 4 km and penetration abilities of 650-750 mm behind explosive reactive armor (ERA). The BMP-3 also features a coaxial 30 mm cannon and a 7.62 mm machine gun. The 30 mm cannon has a firing rate of 330 rounds per minute and is effective against ground targets up to 2 km and low-flying helicopters up to 4 km away.
Advanced Features
The BMP-3 incorporates a computerized fire control system with a ballistic computer, enhancing accuracy and target engagement capabilities. Its advanced armament and fire control make it a formidable force on the battlefield.
Protection and Survivability
Compared to its predecessors, the BMP-3 offers superior protection. The hull and turret are constructed from welded aluminum alloy armor, with composite armor on the front arc providing protection against 30 mm armor-piercing rounds. All-round protection is against 14.5 mm armor-piercing rounds. Additionally, the BMP-3 can be equipped with an add-on explosive reactive armor kit for enhanced protection. The vehicle also features NBC protection and automatic fire suppression systems.
Despite its robust protection, the BMP-3 is known to have a propensity for explosions when its armor is penetrated or when it encounters anti-tank mines, primarily due to its carousel-type autoloader located in the center of the vehicle.
BMP-3 Amphibious Capabilities
The BMP-3 retains its amphibious capabilities, a hallmark of the BMP series (BMP 1, BMP 2 and BMP 3) . On water, it relies on two waterjets for propulsion. However, operational challenges have limited the vehicle’s use of this feature.
Crew and Troop Accommodation
With a crew of three (commander, gunner, and driver) and room for seven troops, the BMP-3 aims to combine mobility with infantry support. Two infantrymen operate bow-mounted machine guns, while the remaining troops sit in the rear compartment. Access is through rear doors and roof hatches, though the limited space remains a drawback.
Power and Mobility
The BMP-3 is powered by a UTD-29 V-10 diesel engine, producing 500 hp. A manual transmission with four forward and two reverse gears is employed, and the IFV features a hydropneumatic suspension, allowing adjustments for different terrains. It is also equipped with a self-entrenching blade for preparing defensive positions.
Ongoing Legacy
While the BMP-3 has enjoyed a successful career, it is gradually becoming outdated. The introduction of the Kurganets-25 IFV in 2015 signaled the need for more advanced platforms. However, funding constraints have limited the fielding of the Kurganets-25 in large numbers, ensuring the BMP-3’s continued presence on the battlefield.
BMP-3 Variants
BMP-3K: Command vehicle.
BMP-3F: A marine version with improved amphibious capabilities.
BMP-3M: An improved export version with a more potent engine and fire control system.
BRM-3 Rys: An armored reconnaissance vehicle with the 100 mm gun removed.
BREM-L Beglyanka: Armored recovery vehicle.
Various specialized versions, including self-propelled howitzers, anti-aircraft guns, anti-tank missile carriers, and more.
Summary of the BMP-3
The BMP-3 infantry fighting vehicle stands as a versatile and formidable asset on the modern battlefield. Its evolution from a light tank replacement to an agile and well-armed IFV demonstrates the flexibility and adaptability of Soviet engineering. While newer platforms are on the horizon, the BMP-3’s legacy