Frigates are the versatile workhorses of modern navies, combining speed, agility, and firepower to execute a wide range of missions, from anti-submarine warfare to escort duties. In recent years, several naval powers have developed and deployed advanced frigate classes that boast an impressive array of capabilities. In this article, we will explore the most powerful frigate classes. The world’s five most powerful frigates are the Admiral Gorshkov class, Sachsen class, Iver Huitfeldt class, Álvaro de Bazán class, and Aquitaine class.
List of the 5 Most Powerful Frigates
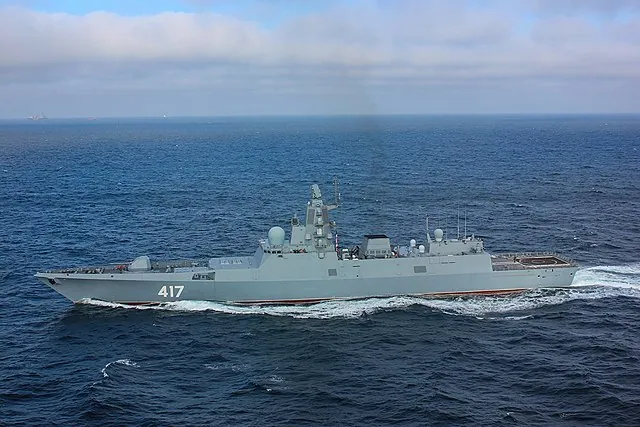
Admiral Gorshkov Class (Russia)
The Admiral Gorshkov class frigate is the most powerful frigate in the world.
Named in honor of Admiral Sergey Gorshkov, the Admiral Gorshkov class frigate is the successor to the Burevestnik class. From long-range surface attacks to anti-submarine warfare, escort missions, and beyond, this class of frigates can step into multipole roles that often necessitate larger destroyers.
The 16-cell Vertical Launch System (VLS) lies at the heart of Admiral Gorshkov class’s offensive capabilities. It houses an array of lethal armaments. These include the Kalibr-NK land attack cruise missiles, the P-800 Oniks anti-ship missiles, and the 91RTE2 anti-submarine missiles.
The Admiral Gorshkov class frigate is equipped to fend off both submarine threats and incoming torpedoes with the inclusion of two quadruple 330 mm torpedo launchers armed with the unique Paket-NK torpedoes.
To fortify its defenses, the Admiral Gorshkov class frigate is armed with the A-192M 130 mm gun, which bolsters its offensive and defensive capabilities. Furthermore, two Palash Close-In Weapon Systems (CIWS) are mounted at the rear, providing a last-ditch defense with their 30 mm rapid-firing Gatling guns and eight short-range surface-to-air missiles (SAMs) each.
In recognition of the vital role of aerial support, the Admiral Gorshkov class frigates are designed to accommodate a single Kamov Ka-27 naval helicopter or a similar variant. This airborne asset enhances the frigate’s surveillance, reconnaissance, and anti-submarine capabilities.
Sachsen Class (Germany)
The Sachsen class frigates, developed in Germany, epitomize air warfare capabilities with a touch of versatility. While based on the Brandenburg class design, these frigates, numbering three, are more akin to destroyers in terms of displacement and firepower. Although sharing commonalities with the Dutch De Zeven Provincien class anti-air warfare destroyers, they are designated as frigates, possibly due to political considerations.
At the heart of their air defense lies the Thales advanced phased-array radar, encompassing 360° target detection, tracking, and engagement. The Thales SMART-L radar further enhances surveillance with its impressive range of over 400 km, capable of detecting and tracking ballistic missiles. Their primary surface-to-air missile armament comprises Standard SM-2 missiles and RIM-162 Evolved Sea Sparrow missiles, nestled in a 32-cell vertical-launch system, alongside two 21-cell Rolling Airframe Missile (RAM) launchers.
Equipped for diverse roles, the Sachsen class frigates wield RGM-84D Harpoon anti-ship missiles, a 76 mm OTO Melara dual-purpose gun, and two Rheinmetall 27 mm guns. Their anti-submarine capabilities include two helicopters, triple 324 mm mountings for EUROTORP MU90 lightweight torpedoes, and advanced sonar systems.
In the realm of sensors and armament, the Sachsen class aligns closely with the Dutch De Zeven Provincien class and Danish Iver Huitfeldt class, boasting an advantage with two helicopter hangars, accommodating NFH 90 or Sea Lynx Mk.88A helicopters. The Sachsen class frigates stand as a testament to Germany’s commitment to cutting-edge naval technology, with their adeptness in air warfare and ability to undertake multifaceted missions on the high seas.
Iver Huitfeldt Class (Denmark)
The Iver Huitfeldt class frigates, an integral part of the Danish navy, boast an economic advantage by sharing hulls with the Absalon class support ships, reducing design and construction costs. Primarily geared for air defense, this class of frigates maintains an unusual layout and robust appearance, although it falls slightly short of the capabilities of its German and Dutch counterparts.
The Iver Huitfeldt class frigates are equipped with advanced anti-air warfare sensors, akin to the German Sachsen class and Dutch De Zeven Provincien class destroyers. With a modular mission payload system, it accommodates six modules, featuring main air defense weapons such as Standard SM-2 (or SM-6) and RIM-162 Evolved Sea Sparrow missiles, alongside Harpoon anti-ship missiles. Its hangar accommodates helicopters like the NFH 90, Westland Lynx Mk.90B, and recently ordered Sikorsky MH-60R Seahawk anti-submarine helicopters, enhancing its anti-submarine warfare capability.
Although propelled solely by four MTU 20V M70 diesel engines, generating 44,000 shp, the Iver Huitfeldt class showcases impressive fuel efficiency, covering 16,700 km (9,000 nautical miles) at lower speeds. Despite slight limitations in comparison to the German Sachsen class frigates, notably in missile defense and propulsion, the Iver Huitfeldt class compensates with advanced air defense radars, underscoring Denmark’s commitment to a well-balanced and efficient naval force.
Álvaro de Bazán Class (Spain)
The Alvaro de Bazan class frigates, an epitome of Spanish naval ingenuity, excel as anti-air warfare vessels designed for escort missions. Spain’s aspiration for a technologically advanced and domestically influenced warship has materialized in the form of these frigates, with five currently serving the Spanish Navy.
Although designated as frigates, the Alvaro de Bazan class frigates share considerable commonalities in terms of displacement and firepower with the Dutch De Zeven Provincien class anti-air warfare destroyers, hinting at their substantial capabilities.
Central to their air defense prowess is the US Aegis system, renowned for its world-class capabilities, also in service with the US Navy, Japan’s Kongo class, and South Korea’s Sejong the Great class. The Aegis system masterfully detects and engages aerial, surface, and submarine threats, tracking air targets at over 300 km and simultaneously managing numerous targets.
Incorporating the Evolved Sea Sparrow Missile (ESSM) for surface-to-air defense and the Standard SM-2MR missiles for area air defense, the Alvaro de Bazan frigates are also equipped with Harpoon anti-ship missiles. Complementing their armament is a 127 mm gun, torpedoes, and other vital weaponry.
The influence of the Alvaro de Bazan class is widespread, forming the foundation for Norway’s Fridtjof Nansen class frigates and Australia’s Hobart class air warfare destroyers, showcasing Spain’s role as a beacon of naval innovation.
Aquitaine Class (France)
The French Aquitaine class frigates, born from the Franco-Italian multi-mission frigate program that also produced Italy’s Carlo Bergamini class, stand as technological marvels in naval engineering.
Underneath their label, the Aquitaine class frigates reveal their destroyer-like capabilities, designed to excel in anti-air warfare, anti-submarine warfare, and land attack missions, with the remarkable ability to strike targets over 1,000 km away. Striking a balance between stealth and innovation, these vessels feature reduced radar cross-section and noise levels, showcasing their technologically advanced design.
Key to their combat readiness is the Thales Herakles multi-purpose passive Electronically Scanned Array (AESA) radar. The radar is capable of tracking air and surface targets at distances of up to 250 km and facilitating fire control for Aster 15 medium-range air defense missiles.
Equipped with a potent arsenal, the Aquitaine class frigates boast a 16-cell Vertical Launch System (VLS) loaded with Aster 15 missiles for air defense and another 16-cell VLS laden with SCALP Naval land attack cruise missiles with a staggering range of over 1,000 km.
Anti-ship capabilities are executed through two quad launchers housing MM.40 Exocet Block 3 anti-ship missiles, effective at ranges exceeding 200 km. A single OTO Melara Super Rapid 76 mm dual-purpose gun, along with three Nexter Narwhal 20B remote weapon systems, ensure a versatile response to a spectrum of threats.
Enhanced by both hull and towed array sonars for submarine detection and twin 324 mm tubes for EUROTORP MU90 lightweight torpedoes, the Aquitaine class frigates seamlessly combine lethality with versatility.
A hangar accommodating a single NH90 NFH helicopter further elevates their anti-submarine and anti-ship capabilities.
Summary of the World’s 5 Most Powerful Frigates
In conclusion, as naval warfare evolves and technology advances, frigates play a crucial role in maintaining maritime security and projecting power on the high seas. The Admiral Gorshkov class, Sachsen class, Iver Huitfeldt class, Álvaro de Bazán class, and Aquitaine class frigates stand out as the most powerful and technologically advanced vessels in their class, showcasing the capabilities of their respective navies. With their versatile mission profiles and cutting-edge systems, these frigates are poised to shape the maritime landscape for years to come.