Bangladesh and China share a long-standing history of trade relations dating back to ancient times. In recent years, the two countries have strengthened their economic ties through trade and investment. In this article, we will discuss the current state of Bangladesh-China trade relations, including the challenges and opportunities, and the future prospects for this relationship.
Bilateral Trade between China and Bangladesh
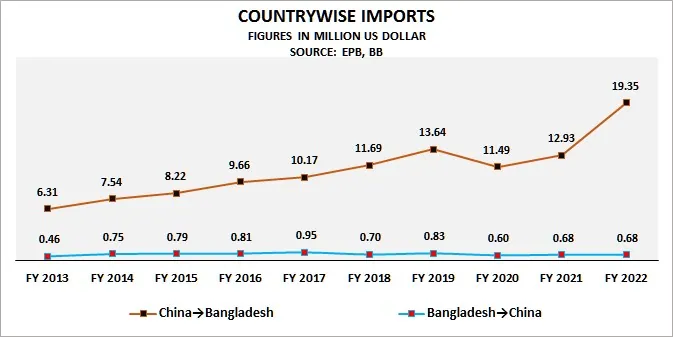
In recent years, Bangladesh and China have made significant progress in their economic cooperation. China is one of Bangladesh’s largest trading partners, and Bangladesh is China’s third-largest trading partner in South Asia after India and Pakistan. However, the trade balance is heavily in favor of China, with a trade deficit of $16.9 billion for Bangladesh in 2019-2020.
China’s export to Bangladesh
China’s exports to Bangladesh have been on the rise in recent years, with China becoming one of Bangladesh’s largest trading partners. In 2019-2020, China’s exports to Bangladesh were valued at $18.1 billion, a significant increase from $7.5 billion in 2012-2013.
The bulk of China’s exports to Bangladesh are manufactured goods, including textiles, electronics, and machinery. These goods are in high demand in Bangladesh, which has a rapidly growing economy and a large population. China is well-positioned to meet this demand, thanks to its vast manufacturing capabilities and competitive pricing.
The textile industry is one of the major sectors where China’s exports to Bangladesh dominate. China is a major producer of textile machinery and equipment, and it exports these products to Bangladesh to support its textile industry. Chinese textile machinery and equipment are known for their quality and reliability, and they help Bangladesh’s textile industry to improve its productivity and efficiency.
Apart from textiles, China’s exports to Bangladesh also include electronics and machinery. Bangladesh’s growing construction industry has driven demand for Chinese construction equipment, such as cranes, excavators, and bulldozers. China is also a major exporter of electronic products, including smartphones, computers, and accessories, which are in high demand in Bangladesh.
Bangladesh’s export to China
Bangladesh’s exports to China have been steadily increasing over the years, as the two countries have strengthened their economic ties. In 2019-2020, Bangladesh’s exports to China were $1.2 billion, a significant increase from $0.5 billion in 2012-2013.
Jute is one of the major exports of Bangladesh to China, as it is used in the production of various products such as carpets, packaging materials, and clothing. Bangladesh is the largest producer and exporter of raw jute in the world, and China is one of the major importers of jute from Bangladesh.
Leather and leather goods are also major exports of Bangladesh to China. Bangladesh’s leather industry has been rapidly growing in recent years, and it has become one of the country’s major export earners. China imports a significant amount of leather from Bangladesh, which is used in the production of various leather goods such as bags, shoes, and belts.
Seafood is another significant export of Bangladesh to China. Bangladesh has a large coastal area, and its fishing industry is growing rapidly. The country exports a wide range of seafood to China, including fish, shrimp, and crab.
Bangladesh’s textile industry is also emerging as a potential source of export to China. Bangladesh is known for its high-quality garments and textiles, and it is seeking to expand its export market in China. In recent years, Chinese companies have been investing in Bangladesh’s textile industry, setting up joint ventures and expanding production capacity.
Investment relations
Chinese investment in Bangladesh has been growing rapidly in recent years, with China emerging as one of the country’s largest sources of foreign direct investment (FDI). Chinese companies have been investing in various sectors in Bangladesh, including infrastructure, energy, and manufacturing, among others.
One of the major areas of Chinese investment in Bangladesh is infrastructure development. Chinese companies have participated in the construction of several major infrastructure projects in the country, including the Padma Bridge, the largest infrastructure project in the country’s history.
Energy is another area where Chinese companies have been investing in Bangladesh. China National Petroleum Corporation (CNPC) and China National Offshore Oil Corporation (CNOOC) have both invested in the country’s energy sector, including the exploration and production of oil and gas. China has also helped Bangladesh in the construction of several power plants.
In addition to infrastructure and energy, Chinese companies have also been investing in manufacturing and other sectors in Bangladesh.
Chinese investment in Bangladesh has provided significant benefits to the country’s economy, creating jobs and contributing to economic growth and development. However, there are also concerns about the sustainability and transparency of Chinese investment in Bangladesh, as well as the potential environmental and social impacts of Chinese-backed projects.
Challenges for China-Bangladesh trade relations
One of the significant challenges for China-Bangladesh trade relations is the trade imbalance. Bangladesh has been trying to reduce the trade deficit by increasing its exports to China. However, due to the lack of value-added exports and the high cost of production, it has not been successful in this regard. Bangladesh’s exports to China mainly consist of raw materials, which have a low market value, whereas China exports manufactured goods, which have a high market value.
Another challenge in China-Bangladesh trade relations is non-tariff barriers, such as regulations and technical standards that can make it difficult for Bangladeshi exporters to access the Chinese market. This has been a particular challenge for Bangladesh’s agricultural exports, as China has strict requirements for food safety and quality.
Lack of infrastructure and investment in Bangladesh are two other major challenges in strengthening China-Bangladesh trade relations. Bangladesh is in dire need of foreign investment to develop its infrastructure and improve its production capacity. China has been investing in infrastructure projects in Bangladesh, including the Padma Bridge and the Payra seaport. However, there have been concerns about the transparency and environmental impact of these projects.
Potentials of Bangladesh-China trade relations
On the other hand, Bangladesh offers several opportunities for Chinese businesses. With a population of over 160 million, Bangladesh has a large consumer market. China can take advantage of this market by investing in manufacturing industries and producing goods for the local market. It will also help reduce trade gap between the two countries. Bangladesh also offers a low-cost labor force, which can be beneficial for Chinese companies seeking to reduce their production costs.
China is the world’s largest consumer market, and there is significant potential for Bangladesh to increase its exports to China. This could include not only traditional exports such as textiles and garments, but also other products such as agricultural goods, seafood, and ICT services.
The future prospects for Bangladesh-China trade relations are promising, given the potential opportunities for both countries. Bangladesh has set a target to achieve $40 billion in trade with China by 2030. To achieve this target, Bangladesh needs to diversify its exports and focus on value-added exports.
China has significant expertise and experience in infrastructure development, which is a key area for Bangladesh’s economic growth and development. Chinese investment in infrastructure projects such as highways, railways, and ports has the potential to improve connectivity within Bangladesh and with other countries in the region.
Chinese companies have already set up joint ventures with Bangladeshi companies, which can help transfer technology and expertise and promote local capacity building. This can have a positive impact on Bangladesh’s economic development and employment opportunities