Land-attack cruise missiles (LACMs) play a crucial role in modern warfare, enabling nations to strike targets deep within enemy territory with precision and effectiveness. In this article, we will delve into the top 10 LACMs in 2025, assessing their capabilities and examining their impact on military operations.
LACM Technology and Functionality
The land-attack cruise missile is an unmanned, armed aircraft crafted to strike fixed or mobile ground-based targets.LACMs are sophisticated weapons designed to be launched from air, sea, or land platforms, providing long-range strike capabilities against a wide range of targets. They combine advanced guidance systems, propulsion technologies, and high-explosive warheads to deliver devastating precision strikes.
The Top 10 Land-Attack Cruise Missiles
The top 10 land-attack cruise missiles in the world in 2024 are Tomahawk, BrahMos , Kh-101, Storm Shadow, JASSM, Delilah, RGM-109E Tomahawk , SOM, YJ-18, and Naval Strike Missile.
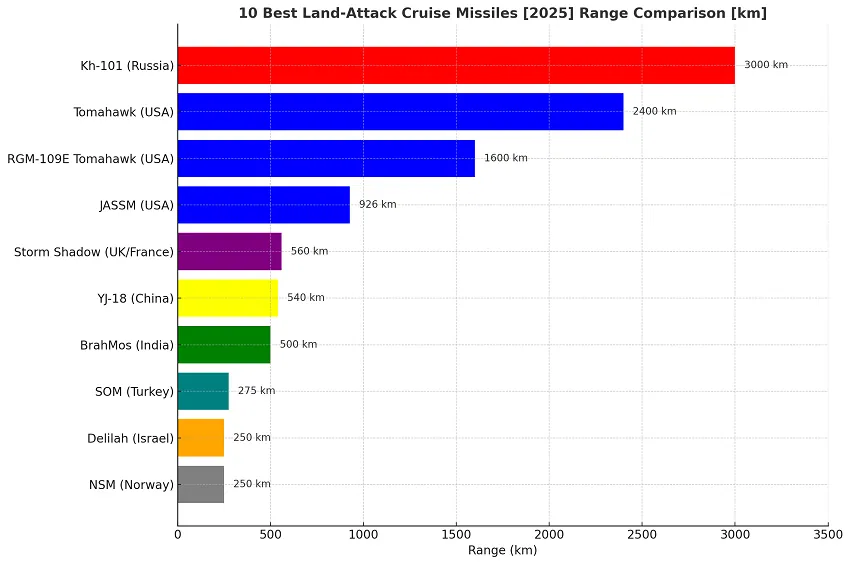
To determine the top 10 LACMs, we considered several key criteria: range, accuracy, payload capacity, guidance systems, and operational history. These factors are vital in assessing the overall effectiveness and tactical value of each missile.
Tomahawk (U.S.)
The Tomahawk Land Attack Missile (TLAM) is a long-range, all-weather, subsonic cruise missile. The United States Navy and Royal Navy use TLAMs primarily. These missiles have been in service since the 1980s. They have undergone several upgrades for enhancement over the years.
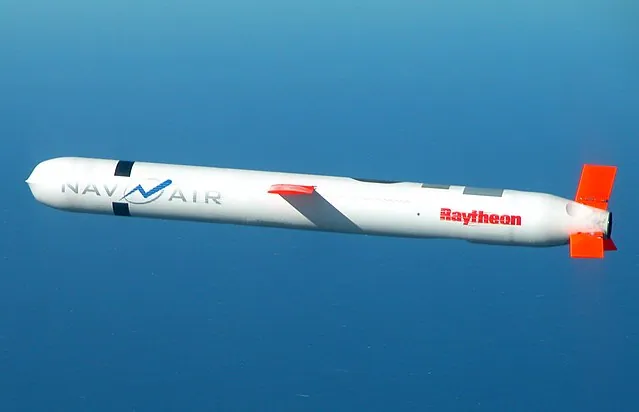

The Tomahawk, with its extended range, versatile payload options, and proven operational history, has become the gold standard for land-attack cruise missiles. TLAMs can fly at extremely low altitudes at high subsonic speeds.
The Tomahawk family includes many different types. The Block III TLAM-C has a 1,000-pound unitary warhead and the TLAM-D submunition dispenser. The Block IV (TLAM-E) has in-flight retargeting and loitering capability. The newest Block V series has better navigation and communications, and there will be future sub-variants like the maritime-strike Block Va and the JMEWS-equipped Block Vb.
It can engage a variety of targets, including enemy defenses, strategic infrastructure, and military installations.
-
Country: United States
-
Range: ~2,400 km (1,500 miles)
-
Speed: Subsonic, ~885 km/h (550 mph)
-
Warhead: 450 kg (1,000 lb) conventional (unitary or submunitions)
-
Guidance: GPS, inertial navigation, terrain contour matching (TERCOM), DSMAC
-
Launch Platform: Ships, submarines
-
Notable Feature: Proven in combat since the 1980s, with over 2,000 used in conflicts like Desert Storm.
BrahMos (India/Russia)
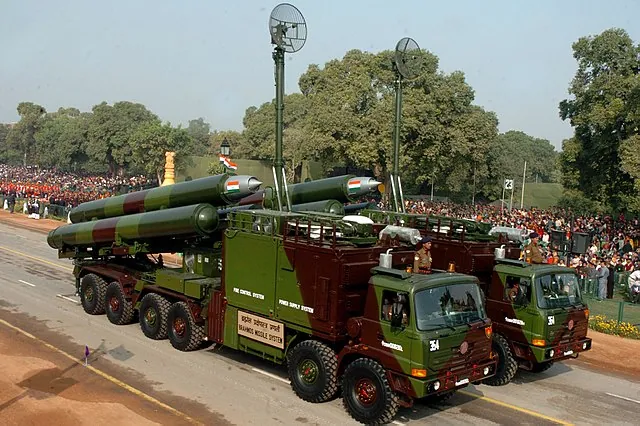

The BrahMos missile stands out for its supersonic speed, making it difficult for enemy air defense systems to intercept. It possesses exceptional accuracy and has been successfully deployed by the Indian Armed Forces.
On May 7, during the Operation Sindoor, India used its cutting-edge BrahMos missile to attach target inside Pakistan.
-
Country: India/Russia
-
Range: 300–500 km (upgraded to 800+ km for air-launched versions)
-
Speed: Supersonic, Mach 2.8 (~3,430 km/h)
-
Warhead: 200–300 kg conventional
-
Guidance: Inertial navigation, active radar homing, GPS/satellite
-
Launch Platform: Land, sea, air, submarine
-
Notable Feature: 32 times the kinetic energy of Tomahawk due to high speed, making it hard to intercept.
Kh-101 (Russia)
The Kh-101 exhibits a long-range, low radar cross-section, and high precision, making it a formidable weapon. It has been utilized effectively in real-world scenarios, showcasing its destructive power against a variety of targets. Russia is also the producers of several fastest missiles and longest range missiles in the world .
-
Country: Russia
-
Range: ~2,500–5,000 km
-
Speed: Subsonic, ~700–900 km/h
-
Warhead: 400–1,000 kg conventional
-
Guidance: Inertial, GLONASS, TERCOM, stealth features
-
Launch Platform: Air (Tu-95, Tu-160 bombers)
-
Notable Feature: Low radar cross-section for stealth, used effectively in Syrian conflict.
-
Visual Element: Stealthy missile silhouette with a bomber launch and long-range path.
Storm Shadow/SCALP (European nations)
The Storm Shadow (known as SCALP in France) is a stealthy missile with an extended range and a highly accurate navigation system. Its ability to penetrate enemy defenses and deliver precision strikes on high-value targets is well-established.
-
Country: UK/France
-
Range: ~560 km
-
Speed: Subsonic, ~1,000 km/h (Mach 0.8)
-
Warhead: 450 kg conventional (BROACH penetrator)
-
Guidance: Inertial, GPS, TERCOM, infrared homing
-
Launch Platform: Air (Typhoon, Rafale, Mirage 2000)
-
Notable Feature: Penetrates hardened targets with high accuracy, combat-proven in Iraq and Libya.
-
Visual Element: Fighter jet launching missile with a bunker-busting explosion.
JASSM (U.S.)
The Joint Air-to-Surface Standoff Missile (JASSM) boasts an impressive range and advanced guidance systems. It can engage both stationary and moving targets, making it a versatile choice for land-attack missions.
-
Country: United States
-
Range: ~926 km (JASSM-ER)
-
Speed: Subsonic, ~900 km/h
-
Warhead: 450 kg blast fragmentation
-
Guidance: GPS, inertial, infrared seeker for terminal guidance
-
Launch Platform: Air (B-1B, B-52, F-16, F-15E)
-
Notable Feature: Stealthy design, can hit moving targets, compatible with multiple aircraft.
-
Visual Element: Stealth missile with a jet launch and target-locking crosshair.
Delilah (Israel)
Israel’s Delilah missile offers a unique combination of stealth and loitering capabilities. It can loiter over the battlefield, identify targets, and then deliver precision strikes, providing increased flexibility and adaptability.
-
Country: Israel
-
Range: ~250 km
-
Speed: Subsonic, ~900 km/h
-
Warhead: 30–54 kg conventional
-
Guidance: Electro-optical, inertial, loitering capability
-
Launch Platform: Air (F-16, helicopters)
-
Notable Feature: Loitering ability allows it to identify and strike targets with precision.
-
Visual Element: Missile circling over a battlefield with a zoomed-in target view.
RGM-109E Tomahawk (U.S.)
The RGM-109E Tomahawk Land Attack Missile (TLAM) Block IV incorporates advanced technologies for improved mission planning and target engagement. It features enhanced communications capabilities and can be reprogrammed in-flight.
-
Country: United States
-
Range: ~1,600 km (900 nautical miles)
-
Speed: Subsonic, ~885 km/h
-
Warhead: 450 kg unitary or multi-effects
-
Guidance: GPS, inertial, TERCOM, DSMAC, two-way datalink
-
Launch Platform: Ships, submarines
-
Notable Feature: In-flight reprogramming and loitering for dynamic targeting.
-
Visual Element: Missile with a digital datalink signal and a ship launch.
SOM (Turkey)
The Standoff Missile (SOM) developed by Turkey offers a significant range and the ability to engage both land and sea targets. It incorporates a high-resolution imaging infrared seeker for precise target discrimination.
-
Country: Turkey
-
Range: ~250–300 km
-
Speed: Subsonic, ~900 km/h
-
Warhead: 230 kg conventional (penetrating or fragmentation)
-
Guidance: GPS, inertial, TERCOM, infrared seeker
-
Launch Platform: Air (F-16, F-4, drones)
-
Notable Feature: High-resolution infrared seeker for precise strikes on land and sea targets.
-
Visual Element: Drone or jet launching missile with a thermal imaging target lock.
YJ-18 (China)
The YJ-18 missile showcases China’s advancements in LACM technology. With a combination of supersonic speed and maneuverability, it poses a significant threat to naval assets and land-based targets. It has also has variants for anti-ship missions. It forms a core part of the People’s Liberation Army’s missile inventory.
-
Country: China
-
Range: ~540 km
-
Speed: Subsonic (cruising), supersonic (terminal, ~Mach 3)
-
Warhead: 140–300 kg conventional
-
Guidance: Inertial, satellite navigation, active/passive radar
-
Launch Platform: Ships, submarines
-
Notable Feature: Supersonic terminal sprint makes it difficult to intercept.
-
Visual Element: Missile accelerating in terminal phase with a naval ship launch.
The Naval Strike Missile (NSM) is a compact, sea-launched land-attack cruise missile that has gained international recognition. It possesses excellent sea-skimming capabilities and a highly accurate target acquisition system.
-
Country: Norway
-
Range: ~185–250 km
-
Speed: High subsonic, ~900 km/h
-
Warhead: 125 kg conventional
-
Guidance: GPS, inertial, TERCOM, infrared imaging
-
Launch Platform: Ships, land
-
Notable Feature: Stealthy design with passive sensors, ideal for coastal and land targets.
-
Visual Element: Stealth missile skimming over water with a coastal target.
Summary of the 10 best land attack cruise missiles
The top 10 land attack cruise missiles in 2025 are:
- Tomahawk
- BrahMos
- Kh-101
- Storm Shadow
- JASSM
- Delilah
- RGM-109E Tomahawk
- SOM
- YJ-18
- Naval Strike Missile.